Network rules (previously known as Packet rules) control whether network traffic is allowed or blocked according to the information contained in network packets. This information may include network protocols, source or destination IP addresses, or local and remote ports. Advanced users can manage these rules or create new ones.
Access network rules
- Open AVG AntiVirus and click the Web & Email tile on the main application screen.

- Click
 Settings (the gear icon) in the top-right corner of the screen.
Settings (the gear icon) in the top-right corner of the screen. 
- Click Basic protection ▸ Enhanced Firewall in the left panel.

- Click View Firewall rules.

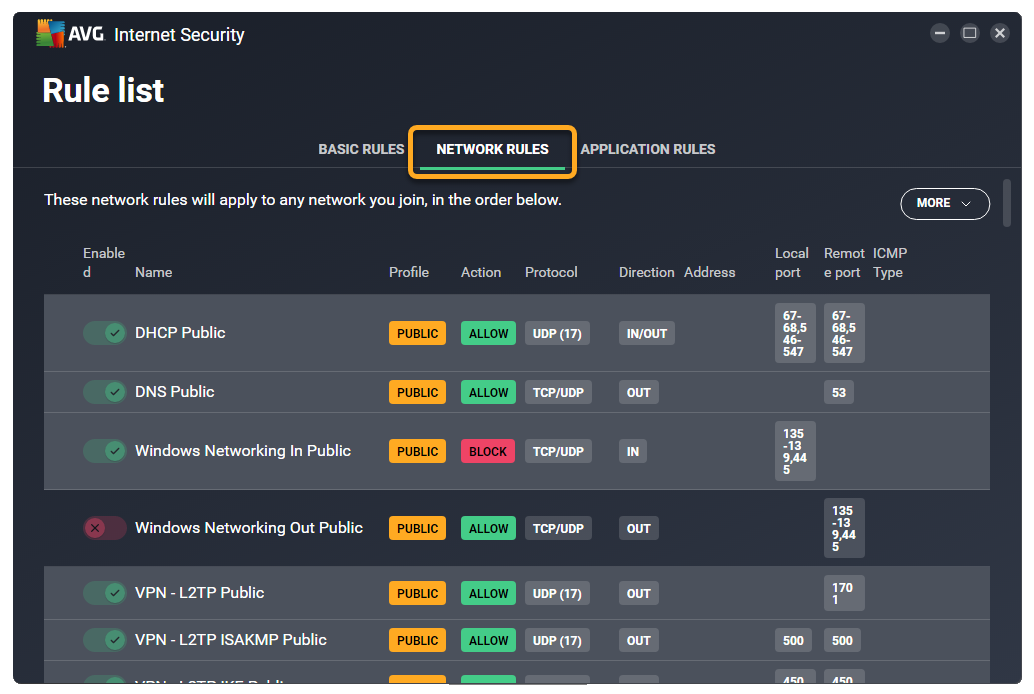
- Select the Network rules tab.

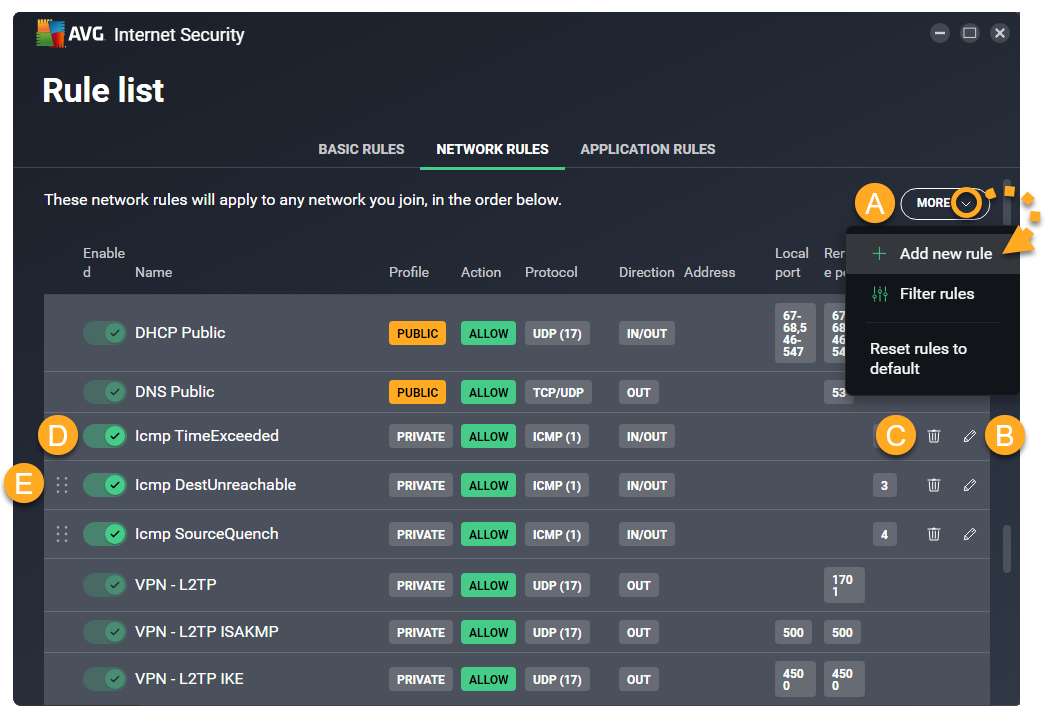
The Network rules screen lists all of your current network rules.
To search for a specific rule, or view only the rules that meet certain criteria, go to More ▸ Filter rules.

For more information about the the network rule parameters, refer to the Review network rules section. To learn how to modify your existing network rules, or create new network rules, refer to the Configure network rules section.
Review network rules
Default network rules provide the extra security needed when you are using a Public (Untrusted) network. Other predefined network rules are created when you change a rule on the Basic rules screen.
Each rule is defined by the following parameters:
- Name: Displays the name of the rule.
- Profile: Indicates which network profile the rule applies to (Public, Private, or All). For more information about network profiles, refer to the following article: AVG Enhanced Firewall - Getting Started ▸ Add trusted and untrusted networks.
- Action: Indicates the action that Enhanced Firewall takes when this rule is applied. Enhanced Firewall may Allow or Block the connection attempt.
- Protocol: Indicates the network protocol used by the corresponding traffic. One protocol may be selected, or All if the rule applies to all protocols.
- Direction: Indicates whether the rule applies to incoming connections (In), outgoing connections (Out), or to connections in both directions (In/Out). For TCP, UDP, or ICMP protocols, this field corresponds to the direction of the first received packet only.
- Address: Indicates the source or destination IP address the rule applies to. The rule may apply to a single IP address, multiple IP addresses (separated by commas), or an IP address range (starting with the lowest IP address and separated with a dash). If the field is blank, the rule applies to all IP addresses.
- Local port: Indicates a network port number on the local IP address of your PC's network interface. The rule may apply for a single port number, multiple ports (separated by commas), or a port range (starting with the lowest port number and separated with a dash). If the field is blank, the rule applies to all local ports.
- Remote port: Indicates a network port number on the remote IP address of the external server or device. The rule may apply for a single port number, multiple ports (separated by commas), or a port range (starting with the lowest port number and separated with a dash). If the field is blank, the rule applies to all remote ports.
- ICMP Type: Indicates the control message (represented by a code number) that the rule applies to. The rule may apply to a single code number, or multiple codes (separated by commas). This option is only available for connections based on the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP). The code numbers of control messages are listed in the technical specifications of the ICMP (RFC 792).
Configure network rules
From the Network rules screen, you can perform the following actions for any network rules that are not default rules:
- Add a new rule: Click More ▸ Add new rule. Define each of the parameters, then click Save to confirm.
- Edit a rule: Click Edit (the pencil icon) in the panel for the relevant rule. Edit the relevant parameters, then click Save to confirm.
- Delete a rule: Click Remove (the trash icon) in the panel for the relevant rule.
- Disable or enable a rule: Click the slider next to a rule to enable/disable it.
- Change rule priorities: Network rules are listed in order of priority, which means that although multiple rules may relate to one packet, the rule that appears highest in the table is always applied first. Click and drag the relevant row up or down to adjust the priority of the selected rule.

- AVG Internet Security 23.x for Windows
- AVG AntiVirus FREE 23.x for Windows
- Microsoft Windows 11 Home / Pro / Enterprise / Education
- Microsoft Windows 10 Home / Pro / Enterprise / Education - 32 / 64-bit
- Microsoft Windows 8.1 / Pro / Enterprise - 32 / 64-bit
- Microsoft Windows 8 / Pro / Enterprise - 32 / 64-bit
- Microsoft Windows 7 Home Basic / Home Premium / Professional / Enterprise / Ultimate - Service Pack 1 with Convenient Rollup Update, 32 / 64-bit