Some websites and servers restrict VPN use. In these cases, you need to use your physical IP address. Rather than disabling your VPN every time you want to access these websites, you can set up a permanent VPN bypass, so your physical IP address is used automatically.
To set up a VPN bypass route, you first need to locate your Gateway IP address and the IP address of the website you want to access.
Disconnect AVG Secure VPN before following the instructions in this article.
Locate your Gateway IP address
Your Gateway IP address is usually the IP address of your router/DSL-Modem, for example, the device that provides internet to your PC. To set up a VPN bypass route, you need to know the IP address of this device. To find your Gateway IP address:
- Click the Windows
 Start icon and type
Start icon and type cmd, then select Command Prompt from the search results. - In the Command Prompt window, type
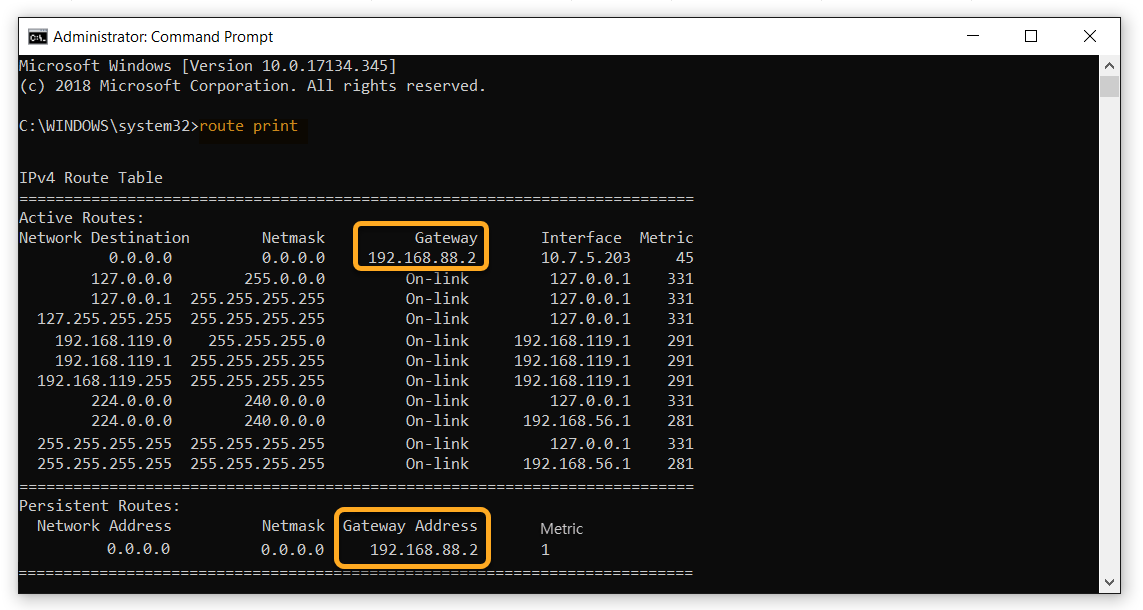
route print and press Enter. - In the IPv4 Route Table output you can find your Gateway IP address under Gateway Address (or Gateway). Take note of this number.

- In the Apple menu bar, select Go ▸ Utilities, then open Terminal.
- In the Terminal window, type
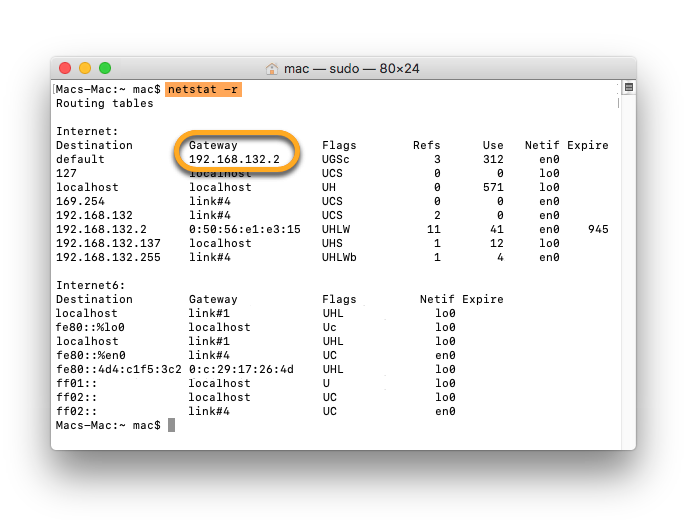
netstat -r, and press Enter. - In the output you can find your Gateway IP address under Gateway. Take note of this number.

Locate the IP address of a website
To set up a VPN bypass route, you need to know the IP address of the website that you want to access. To find an IP address:
- Click the Windows
 Start icon and type
Start icon and type cmd, then select Command Prompt from the search results. - In the Command Prompt window, type
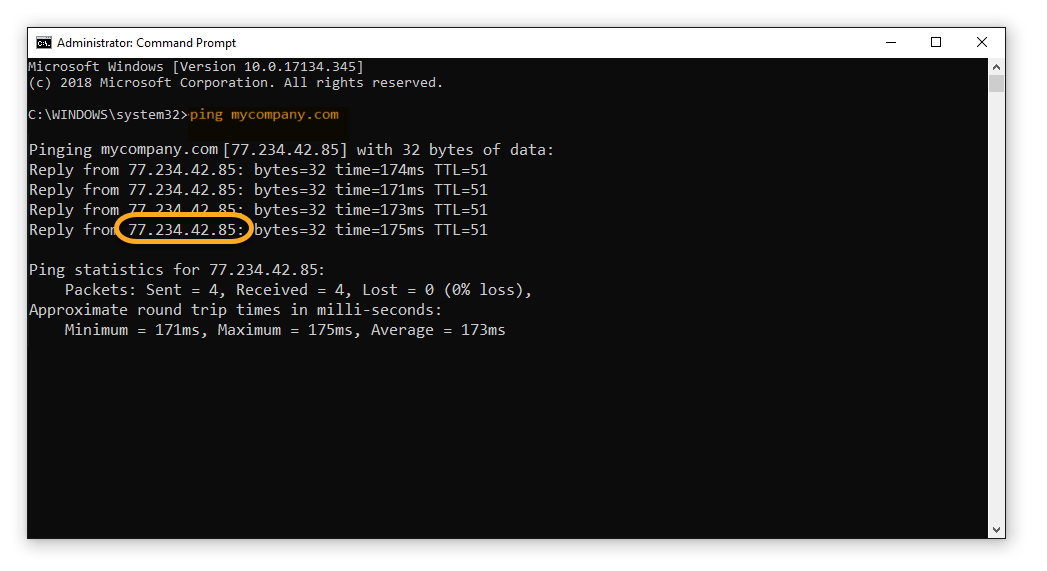
ping followed by the URL of the website you want to set up the VPN bypass for. For example, to find the IP address of the website www.mycompany.com, type ping mycompany.com into the Command Prompt window and press Enter. - In the Command Prompt window you can now see the IP address of the website. Take note of this number.

- In the Apple menu bar, select Go ▸ Utilities, then open Terminal.
- Type
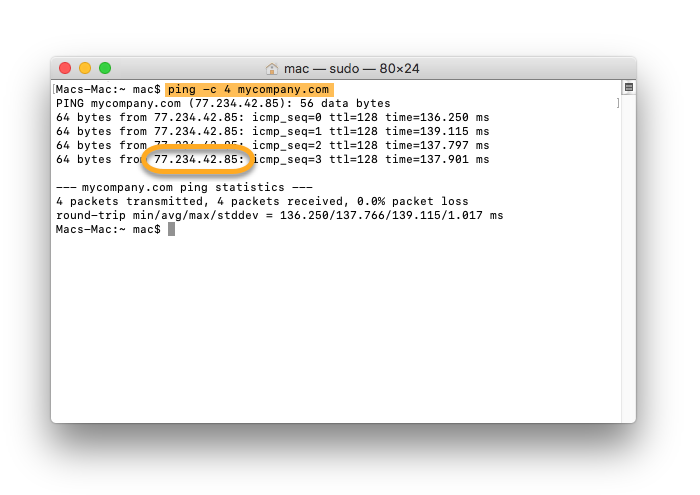
ping -c 4 followed by the URL of the website you want to set up the VPN bypass for. For example, to find the IP address of the website www.mycompany.com, type ping -c 4 mycompany.com into the Terminal window and press Enter. - In the Terminal window you can now see the IP address of the website. Take note of this number.

Set up a VPN bypass route
You can access certain VPN restrictive websites or servers by manually setting up a VPN bypass route. You will need to know your Gateway IP address and the IP address of the website you want to bypass.
- Click the Windows
 Start icon and type
Start icon and type cmd. Select and right-click Command Prompt from the search results, then click Run as administrator. - In the Command Prompt window, type
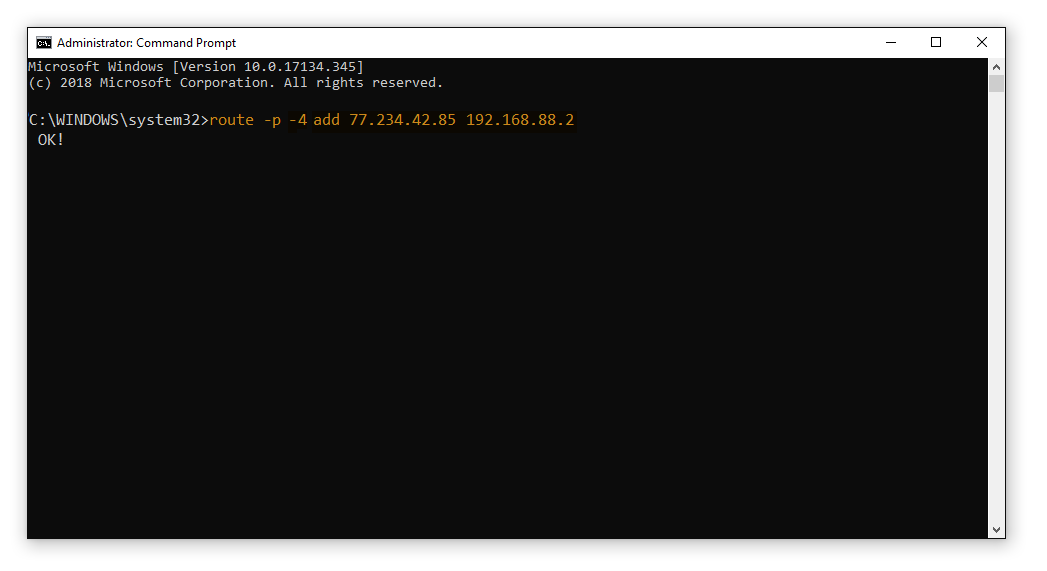
route -p -4 add followed by the IP address of the website, then your Gateway IP address. For example, route -p -4 add 77.234.42.85 192.168.88.2 where 77.234.42.85 is the IP address of the website you want to access and 192.168.88.2 is your Gateway IP address.
If you want to set up a temporary bypass route, remove -p from the route string.
- Press Enter to activate the routing.

Before following the instructions below, ensure you are logged in to your Mac with an administrator account that has a password.
- In the Apple menu bar, select Go ▸ Utilities, then open Terminal.
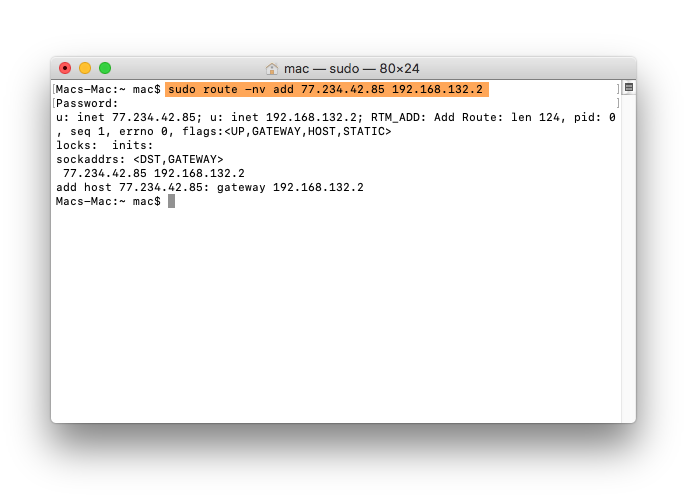
- Type
sudo route -nv add followed by the IP address of the website and then your Gateway IP address. For example, sudo route -nv add 77.234.42.85 192.168.132.2 where 77.234.42.85 is the IP address of the website you want to access and 192.168.132.2 is your Gateway IP address. - Press Enter to execute the command.

- Terminal prompts you for your password. Type your password and press Enter.
The cursor in the Terminal window will not move when you type your password.
The bypass route is set up. You can now connect to your VPN again and you should be able to access the previously blocked website.
Troubleshooting
If the steps above do not work or your bypass route stops working, we recommend you contact the administrator of the website or server you are trying to access. It is possible that the website or server has more than one IP address. In this case you will need to repeat the steps above for each IP address.
- AVG Secure VPN 5.x for Windows
- AVG Secure VPN 1.x for Mac
- Microsoft Windows 11 Home / Pro / Enterprise / Education
- Microsoft Windows 10 Home / Pro / Enterprise / Education - 32 / 64-bit
- Microsoft Windows 8.1 / Pro / Enterprise - 32 / 64-bit
- Microsoft Windows 8 / Pro / Enterprise - 32 / 64-bit
- Microsoft Windows 7 Home Basic / Home Premium / Professional / Enterprise / Ultimate - Service Pack 1, 32 / 64-bit
- Apple macOS 12.x (Monterey)
- Apple macOS 11.x (Big Sur)
- Apple macOS 10.15.x (Catalina)
- Apple macOS 10.14.x (Mojave)
- Apple macOS 10.13.x (High Sierra)
- Apple macOS 10.12.x (Sierra)